Download the Simulink Model:
What is Amplitude Modulation?This topic is the result of Digital Signal Processing term project named Amplitude Modulation and Demodulation on Texas Instrument Kit DSK C6713 with Matlab Simulink. One of the fundamental part of our project is included in this very post. The whole term mini project will be gradually discussed in subsequent posts. Before we proceed, we must know what actually modulation and amplitude modulation is? A modulator alters the carrier waves corresponding to the variation of the modulating signals. Resulting modulated signal thus carries message information. Amplitude modulation is the process of changing the amplitude of a high frequency carrier signal corresponding to the amplitude of the modulating signal (Information). The wave whose amplitude is being varied is called the carrier wave and the signal doing the variation is called the modulating signal i-e message signal or information signal. The carrier is always almost a sinusoidal wave. The modulating or message signal can be a sine wave but it can be arbitrary waveform such as audio signal etc. Some Mathematics :
For simplicity, suppose both carrier wave and modulating signal are sinusoidal:
vc = Vc sin wc t (c denotes carrier)
and
vm = Vm sin wm t (m denotes modulation)
We want the modulating signal to vary the carrier amplitude, Vc, so that:
vc = (Vc + Vm sin wmt).sin wc t
where (Vc + Vm sin wm t) is the new, varying carrier amplitude.
Expanding this equation gives:
vc = Vc sin ωc t + Vm sin ωc t. sin ωm t
which may be rewritten as:
vc = Vc [sin ωc t + m sin ωc t. sin ωm t]
where m = Vm/Vc and is called the modulation index.
sin ωc t.sin ωm t = (1/2) [cos(ωc - ωm) t - cos(ωc + ωm) t]
so, from the previous equation:
vc = Vc [sin ωc t + m sin ωc t. sin ωm t]
we can express vc as:
vc = Vc sin ωc t + (mVc/2) [cos(ωc - ωm) t] - (mVc/2) [cos(ωc + ωm) t]
- The original carrier waveform, at frequency ωc, containing no variations and thus carrying no information.
- A component at frequency (ωc - ωm) whose amplitude is proportional to the modulation index. This is called the Lower Side Frequency.
- A component at frequency (ωc + ωm) whose amplitude is proportional to the modulation index. This is called the Upper Side Frequency.
AMPLITUDE MODULATION USING MATLAB SIMULINK
Lets discuss step by step the implementation of amplitude modulation on simulink modulation :-
Start the new Simulink model
Open the Simulink library browser
Create the simulation model of the AM
Message Signal:
A Sinusoidal signal of frequency 1 Hz, Amplitude=1
Carrier Signal of frequency 20 Hz and Amplitude=1
The above model is the equivalent of the mathematical expression:
s(t)=[1+m(t)](cos(2πfct))
Where;
m(t) represent the message signal
And cos(2πfct) represent the carrier
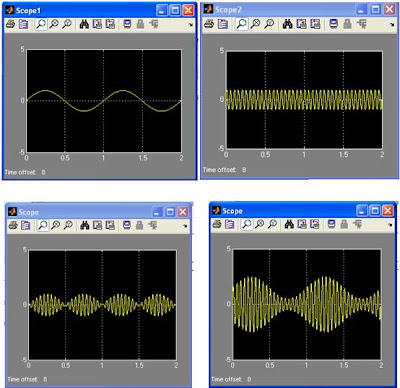
Run the Simulink model, the message, carrier and modulated output can be observed on the oscilloscope.
The above diagtam shows both supressed and without supressed carrier.You are recommended to see the following too :-
- Amplitude Modulation on Matlab Simulink Model
- Amplitude Demodulation on Matlab Simulink Model
- Real-time Amplitude Modulation and Demodulation on Texas Instrument DSK C6713
CERTIFICATE OF OWNERSHIP
This project named “AMPLITUDE MODULATION USING MATLAB SIMULINK AND TEXAS INSTRUMENT KIT C6713”, in all respect is the property of the following personnel who undertake this project as the term project in EE-322 ‘DSP & Filters’ in summer semester 2010. However the copy of the project can be distributed upon the approval of the following members:-
- Muhammad Ahmed (NUST-ELECTRONICS)
- Jamal Ahmed(NUST-ELECTRONICS)
- Muhammad Faisal (NUST-ELECTRONICS)